In June I was recommended by a mutual friend to shoot a short drama called Perplexed Music, inspired by the Elizabeth Barrett Browning sonnet of the same name. It’s a passion project from writer-director Mark McGann, with his brother Paul McGann (Doctor Who, Alien 3, Withnail & I) in the lead role of a man grieving for his deceased partner.

Mark was keen from the outset to shoot on an Alexa, and I was quick to agree. Arri Rental very kindly gave us an amazing deal on an Alexa Classic and a set of Ultra Primes. As on Above the Clouds, we used a Blackmagic Micro Cinema Camera as a B-cam, capturing two specific angles that were impossible on the Alexa with our limited grip budget.
Throughout July, Mark and I had a very satisfying creative dialogue about the cinematic techniques we would use to tell the story of Paul’s character, The Man, who never speaks. I had been watching a lot of Mr. Robot, and was keen to use unusual compositions as that show does. The visual grammar that we ultimately developed eschewed The Rule of Thirds, either squeezing The Man right into the side of frame – at times when things are too much for him – or placing him dead centre for moments of clarity and acceptance, and for flashbacks to when his partner was alive.

While testing lenses at Arri Rental a few weeks prior to the shoot, I took the opportunity to shoot some frame-rate tests between 24 and 48fps. Since the film has so little dialogue, I figured there was nothing to stop us using a lot of slow motion if we wanted to. I didn’t want it to look like a music video though. I thought perhaps a very subtle over-cranking, creating languid blinks and slightly heavier movement, would add to the burden of The Man’s grief. Mark agreed as soon as he saw the tests, and we ended up shooting a number of set-ups at 28 and 30fps, plus 40fps for a pivotal sequence.
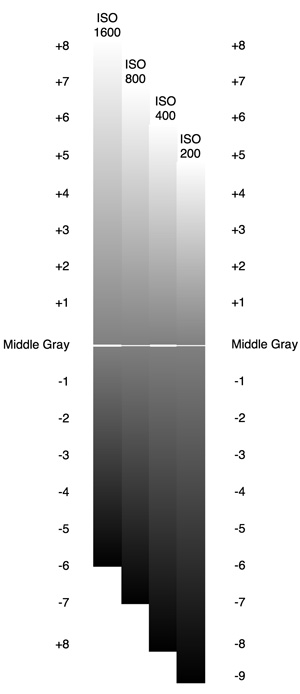
I also tested various ISO settings on the Alexa (click here for full details, stills and video from this test). Based on these, I decided to use ISO 1600 for the majority of the film, partly for the extra latitude in the highlights, and partly to add grittiness to The Man’s grief-stricken world, in the form of a little picture noise. When we started shooting the flashbacks, on the spur of the moment I decided to switch to ISO 400 for these. A few years back I shot the music video below on a Red Epic and, for reasons I forget, one set-up was done at a lower ISO than the rest. I remember the feeling this gave, when I saw the final edit, of everything suddenly being smooth and hyper-real. I thought that would be a great feeling to give to the flashbacks.

Much of Perplexed Music was day exterior, but a couple of sequences required lighting. In the opening café scene, I fired HMIs through two windows, but kept their light away from The Man, keying him with a practical to put him in his own little world. Meanwhile, a happy couple he’s watching are bathed in sunlight (sometimes real, sometimes not) warmed up with a quarter CTO, and bouncing beautifully off their table to give them a healthy glow.
For night interiors at The Man’s home, I was keen to rely on practicals as much as possible. Firstly there wasn’t much space in the little cottage, secondly I didn’t want the hassle of having to shift them around to keep them out of frame when we changed angle, and thirdly it just looks more natural. So aside from a tungsten bounce in a corner of the living room we knew would never be seen, I stuck to practical table lamps and exterior lighting.
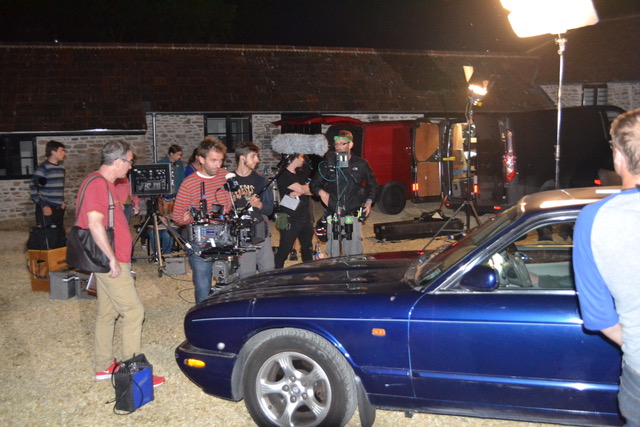

 I had planned to use direct HMI sources for moonlight through the windows, but my gaffer Sam suggested going softer so that we wouldn’t have hard shadows inside which would need filling. I saw that he was right, so we used a kino through one window and a 2.5K HMI bounced into poly through another (pictured at left).
I had planned to use direct HMI sources for moonlight through the windows, but my gaffer Sam suggested going softer so that we wouldn’t have hard shadows inside which would need filling. I saw that he was right, so we used a kino through one window and a 2.5K HMI bounced into poly through another (pictured at left).
Perplexed Music was shot over five days in Frome in Somerset and Rame in Cornwall. The latter provided us with a spectacular cliff-top and the isolated St. Michael’s Chapel on the peak of the headland. Here we employed the services of The Fly Company, who captured two dramatic, sweeping shots on their DJI Inspire 2 drone. We were all extremely impressed by what they were able to achieve, especially as it was done in very windy conditions, in between rain showers.
We completed the final set-ups of the schedule as the winds began gusting up to 60mph, and poor Paul could barely stand upright! I was certainly glad we picked the Alexa to shoot on, because anything lighter would probably have shaken during takes, if not blown over!

I had a fantastic time working with Mark and Paul, and the whole cast and crew. We were sad to part ways at the end of the week, and we all look forward to seeing the finished film soon. And at this point, dear reader, I ask for your help. Currently a Kickstarter campaign is underway for postproduction. It’s well over 50% funded at the time of writing, but every little helps in our quest to reach the finishing line. Rewards for backers include thank you video messages from Paul and Mark, and tickets to a private screening in December. Even if you can’t contribute, please consider sharing the page on social media. Thanks!
https://www.kickstarter.com/projects/perplexedmusic/perplexed-music-post-production