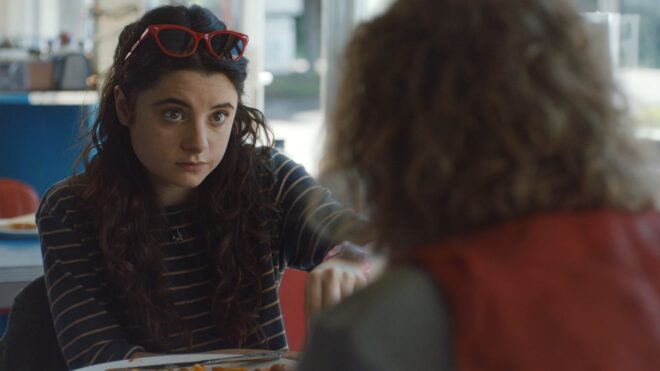If you’ve ever learnt anything about lighting, you’ll have heard of the Three Point System: key, backlight and fill. That last one is a soft light which raises the shadows and reduces contrast in the image.
As you might expect, negative fill is the exact opposite. It brings the shadows down, increasing contrast. It’s a big part of cinematography today because the dynamic range of digital cameras is so wide and their light sensitivity is so high that taking away light has become just as important as adding it.
Negative fill – neg fill or just neg for short – can be accomplished with anything black, most commonly a polystyrene board (American name: bead-board), blackout material (usually bolton in the UK or duvetyne in the US) or a flag. 5-in-1 reflectors have a black side that can be used for neg fill too. The term solids or black solids can be applied to any of these tools, indicating that they are completely opaque, as opposed to nets.
When DPs talk about neg fill you often hear the word “shape” come up in their reasoning. Neg fill is typically applied to the camera side (broad side) of the talent, allowing their other side (short side) to remain bright. This has the effect of making the face – or any other object – look more three-dimensional. Hence “shape”. (This is all part of the theory of short key lighting, which I’ve covered in detail before.)
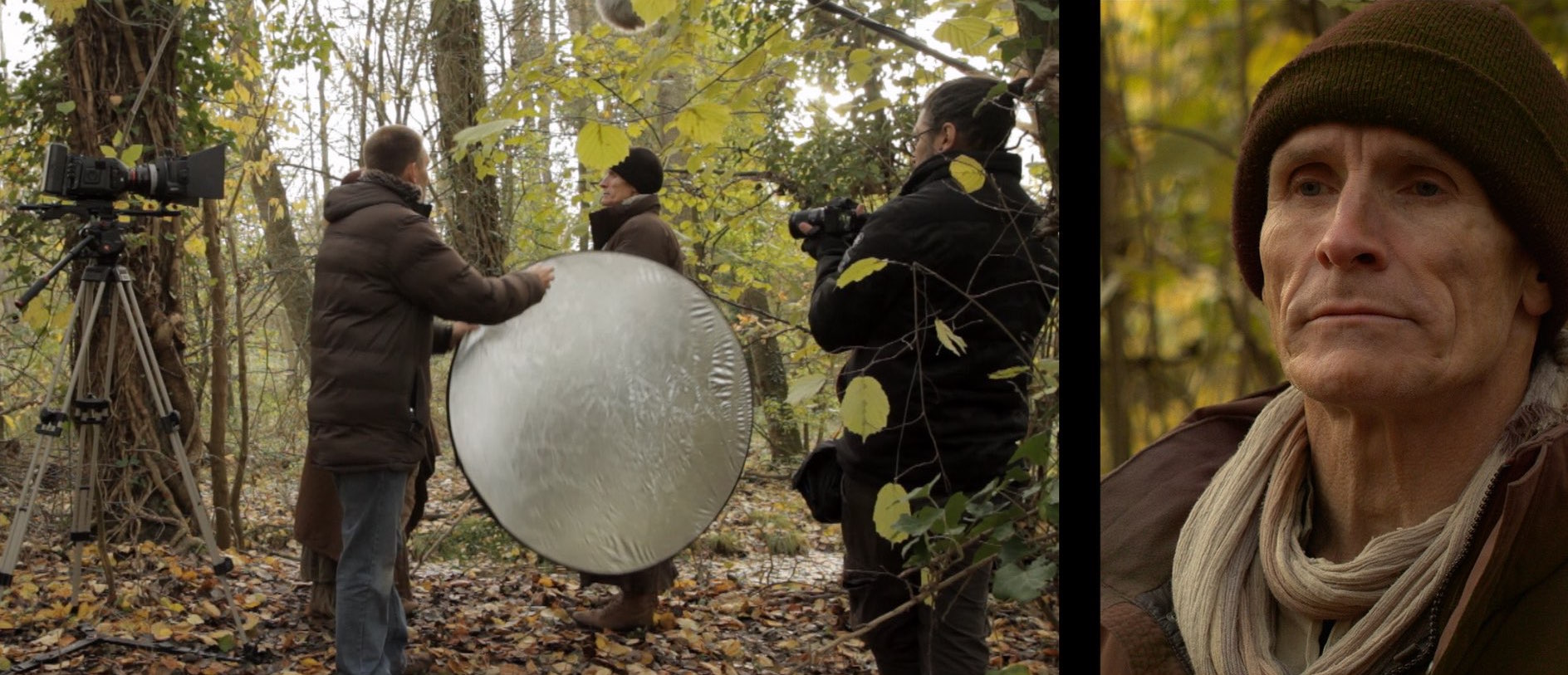
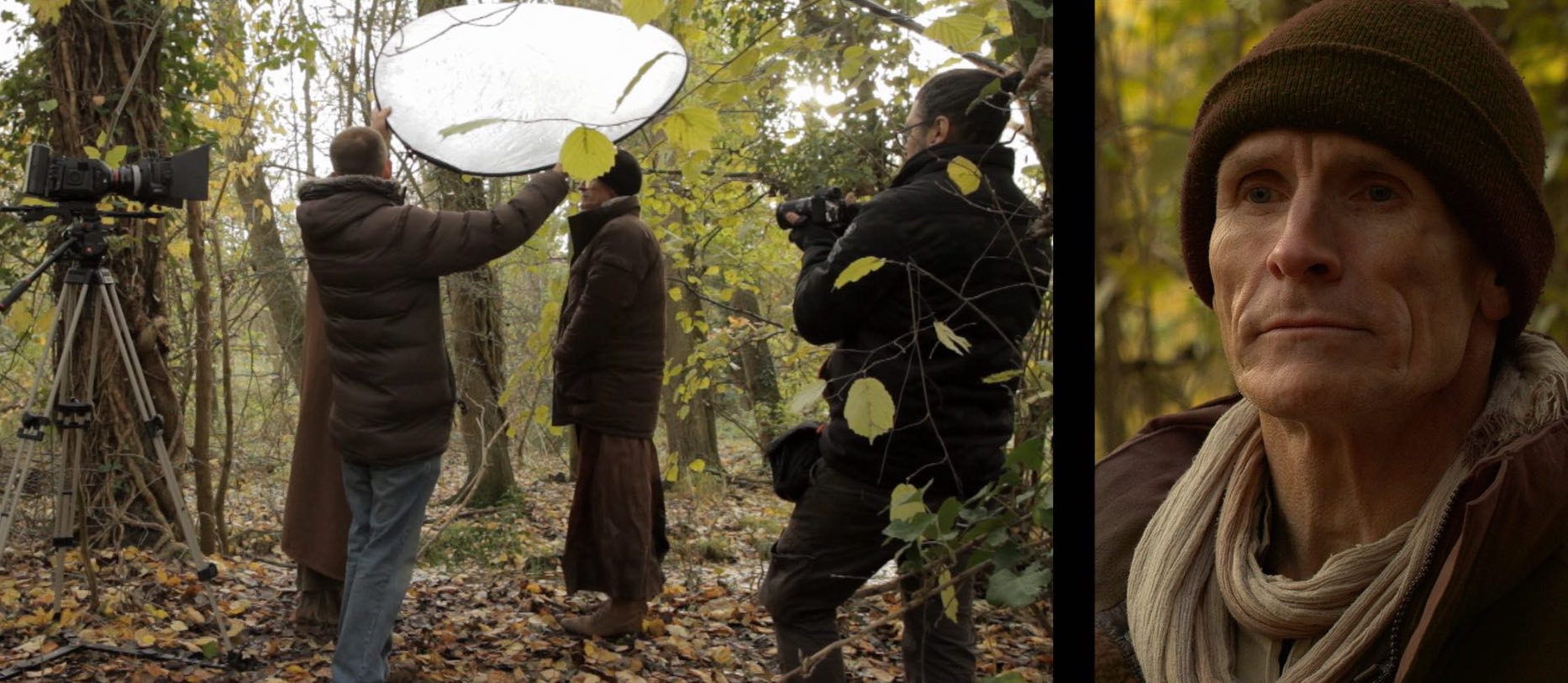
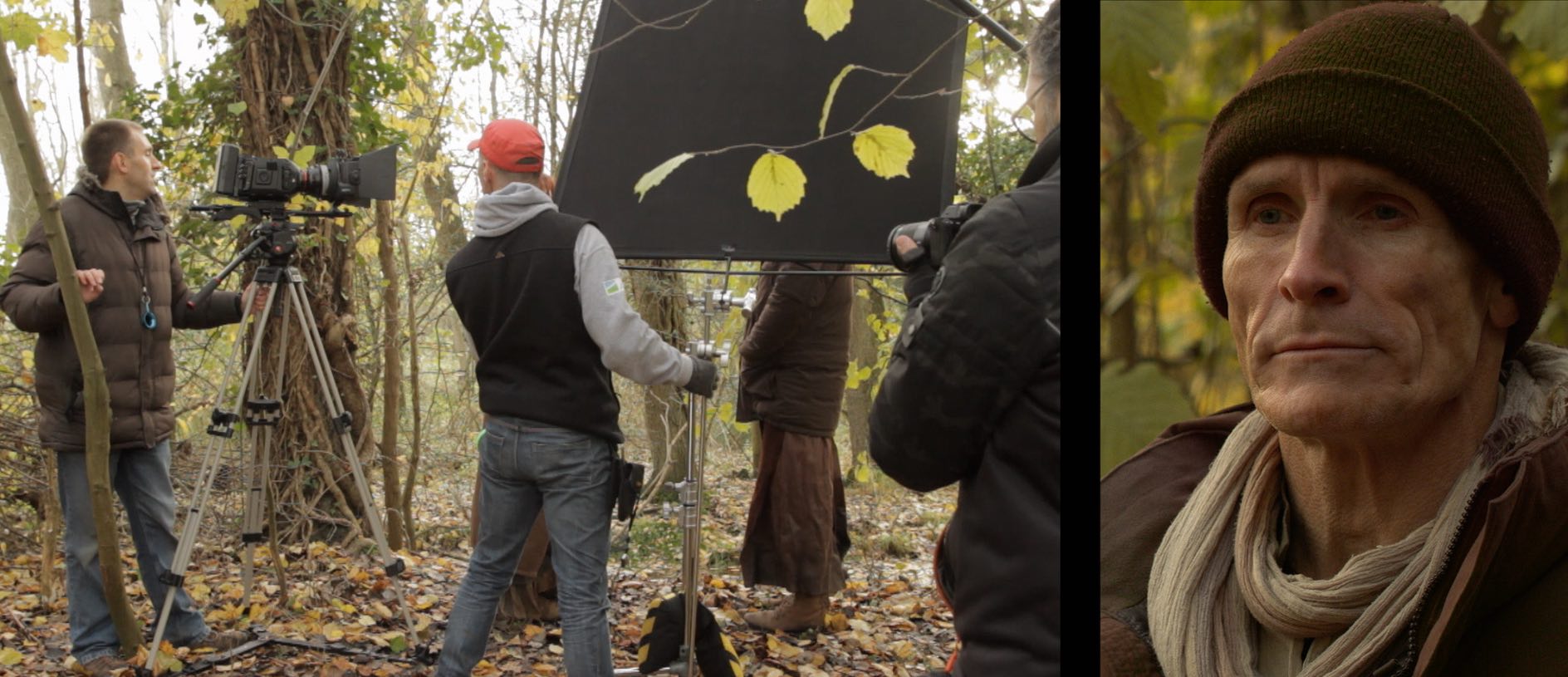
Below is an example from my online course, Cinematic Lighting. In these before and after shots, I use the black side of a 5-in-1 reflector (though you see silver facing camera) to neg-fill Ivan’s short side, adding mood and contrast.
We made it more permanent by replacing the reflector with a 4×4′ floppy flag on a C-stand.
Here’s an example from Heretiks where I chose to put a glint of light back into the darkness created by the neg fill, by using a matt silver reflector to create a rim-light. (There are many more diagrams like this on my Instagram feed.)
Neg fill is most commonly used outdoors, but it can be desirable indoors too, for example when white walls are bouncing light around everywhere. For the shot below from Exit Eve, I had the white wall behind camera covered with bolton so that the light would all be coming from behind the talent. (See my article on lighting from the back.)
In the café scene from Above the Clouds we shot towards the windows, but there was still too much ambience (mainly from skylights in the roof) on the camera sides of the actors for my taste. We only had a limited supply of flags, so we pressed the sides of the Easy-Up tent into service too!
I’ll leave you with this extreme example of negative fill from Instagram.
View this post on Instagram