An updated version of this article is available.
As I was writing my last entry, in which I mentioned the range of colour temperatures in a shot, it occurred to me that some readers might find an explanation of this concept useful. What is colour temperature and why are different light sources different colours?
The answer is more literal than you may expect. It’s based on the simple principal that the hotter something burns, the bluer the light it emits. (Remember from chemistry lessons how the tip of the blue flame was always the sweet spot of the Bunsen Burner?)

Colour temperature is measured in kelvins, a scale of temperature that begins at absolute zero (-273°C), the coldest temperature physically possible in the universe. To convert centigrade to kelvin, simply add 273. So the temperature here in Hereford right now is 296 kelvin (23°C).
The filament of a tungsten light bulb reaches a temperature of roughly 3,200K (2,927°C). This means that the light it emits is orange in colour. The surface of the sun is about 5,778K (5,505°C), so it gives us much bluer light.
Colour temperature isn’t necessarily the same as actual temperature. The atmosphere isn’t 7,100K hot, but the light from the sky (as opposed to the sun) is as blue as something burning at that temperature would be.
Digital cameras have a setting called “white balance” which compensates for these differing colour temperatures and makes them appear white. Typical settings include tungsten, daylight, shade and manual, which allows you to callibrate the white balance by holding a white piece of paper in front of the lens as a reference.

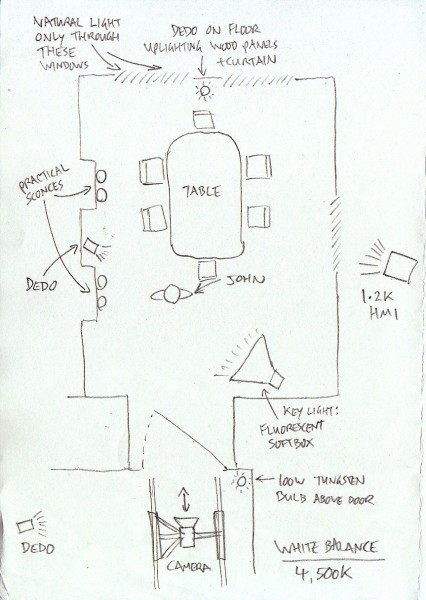
Today there are many types of artificial light around other than tungsten – fluorescent and LED being the main two. In the film industry, both of these can be obtained in flavours that match daylight or tungsten, though outside of the industry (if you’re working with existing practical sources) the temperatures can range dramatically.
There is also the issue of how green/magenta the light is, the classic example being that fluorescent tubes – particularly older ones – can make people look green and unhealthy. If you’re buying fluorescent lamps to light a scene with, check the CRI (colour rendering index) on the packaging and get the one with the highest number you can find for the fullest spectrum of light output.
The Magic Lantern hacks for Canon DSLRs allow you not only to dial in the exact colour temperature you want, but also to adjust the green/magenta balance to compensate for fluorescent lighting. But if two light sources are giving out different temperatures and/or CRIs, no amount of white balancing can make them the same.

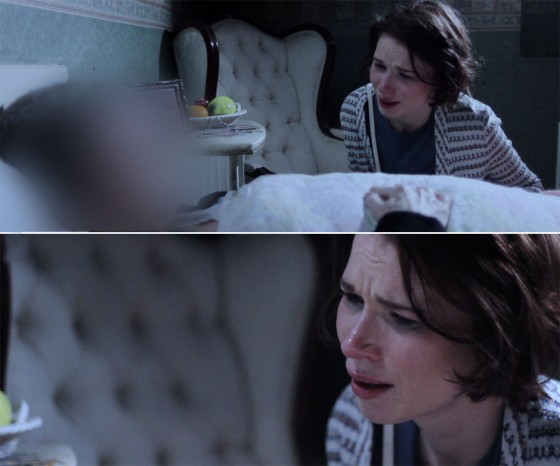
The classic practical example of all this is a person standing in a room with a window on one side of them and a table lamp on the other. Set your camera’s white balance to daylight and the window side of their face looks correct, but the other side looks a nasty orange (above left), or maybe yellowy-green if the lamp has an energy-saving bulb in it. Change the white balance to tungsten or fluorescent and you will correct that side of the subject’s face, but the daylight side will now look blue (above right) or magenta.
This is where gels come in, but that’s a topic for another day.
The beauty of modern digital cinematography is that you can see how it looks in the viewfinder and adjust as necessary. But the more you understand the kind of theory I’ve outlined above, the more you can get it right straight away and save time on set.