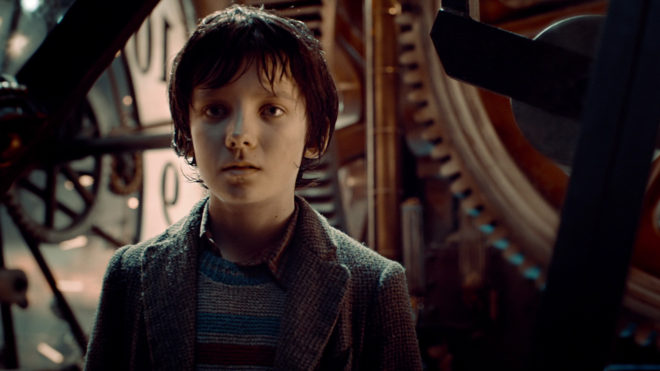This summer I shot Exit Eve, a short film from director Charlie Parham dealing with the exhausting and demeaning life of an au pair. We took the unusual decision to shoot it in 4:3, a ratio all but obsolete, but one which felt right for this particular story. Before I look at some of the ratio’s strengths and challenges, let’s remind ourselves of the history behind it.
History

The 4:3 motion picture aspect ratio, a.k.a. 1.33:1, was created about 120 years ago by William Kennedy Dickson. This Thomas Edison employee was developing a forerunner to the movie projector, and decided that an image height of four perforations on 35mm film gave the ideal shape. In 1909 the ratio was declared the official standard for all US films by the Motion Picture Patent Company.
When the talkies arrived two decades later, room needed to be made on the film prints for the optical soundtrack. The Academy of Motion Pictures Arts and Sciences responded by determining a new, very slightly wider ratio of 1.37:1, known fittingly enough as the Academy Ratio. It’s so similar to 4:3 that I’m going to lump them together from hereon in.
 When television was invented it naturally adopted the same 4:3 ratio as the big screen. The popularity of TV led to falling cinema attendance in the 1950s, to which the Hollywood studios responded with a range of enticing gimmicks including widescreen aspect ratios. Widescreen stuck, and for the next generation 1.85:1 and 2.39:1 were the ratios of cinema, while the narrower 4:3 was the ratio of TV.
When television was invented it naturally adopted the same 4:3 ratio as the big screen. The popularity of TV led to falling cinema attendance in the 1950s, to which the Hollywood studios responded with a range of enticing gimmicks including widescreen aspect ratios. Widescreen stuck, and for the next generation 1.85:1 and 2.39:1 were the ratios of cinema, while the narrower 4:3 was the ratio of TV.
By the time I entered the industry in the late 1990s, 4:3 was much maligned by filmmakers. It seemed boxy and restrictive compared with widescreen, and reminded those of us in the guerrilla world that we didn’t have the budgets and equipment of the Hollywood studios. Meanwhile, the wide compositions of big movies were butchered by pan-and-scan, the practice of cropping during the telecine process to fit the image onto a 4:3 TV without letterboxing. 4:3 was ruining our favourite movies, we felt.
Then, in the 21st century, 16:9 television became the norm, and the 4:3 aspect ratio quietly disappeared, unmourned…. Or did it?
Contemporary Cinema
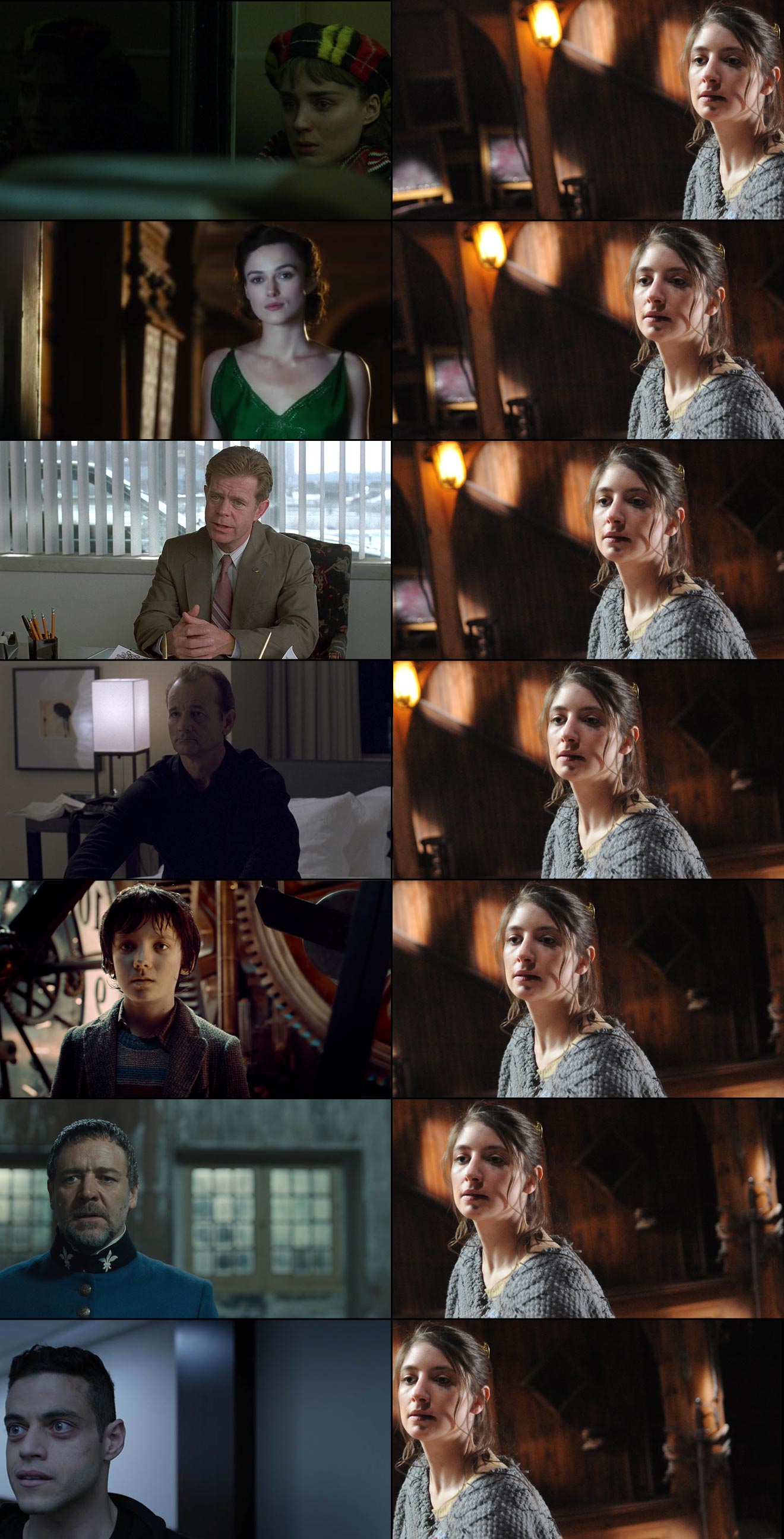
Although they are firmly in a minority, a number of filmmakers have experimented with 4:3 or Academy Ratio in recent years. Some, like Andrea Arnold and the late Éric Rohmer, rarely shot anything else.
Arnold wanted a combination of intimacy and claustrophobia for her Bafta-winning 2009 drama Fish Tank. She carried the ratio over to her next film, an adaptation of Wuthering Heights, despite the prevalence of big landscapes which would have prompted most directors to choose 2.39:1. The Academy Ratio focuses the viewer’s attention much more on the characters and their inner worlds.

Mark Kermode has this to say about the 1.37:1 work of Arnold and her DP Robbie Ryan: “What’s wonderful about it is the way [Ryan] uses that squarer format not to make the picture seem compressed but to make it seem taller, to make it seem larger, to make it seem oddly more expansive.”
Meek’s Cutoff (2010), a modern western by Kelly Reichardt, recalls the early Academy classics of the genre. As with Wuthering Heights, characters are placed in the landscape without being dominated by it, while the height of the frame produces bigger skies and an airier feel.

Pawel Pawlikowski’s 2013 Oscar-winner Ida deliberately goes against the grain, shooting not only in 4:3 but in black and white as well. It’s the perfect format to convey the timeless, spartan existence of the titular Ida and her fellow nuns. The tall frame allows for copious headroom, inspiring thoughts of Heaven and God, beneath which the mortal characters seem small.
The 2017 animated feature Loving Vincent, meanwhile, adopted 4:3 because it was closer to the shape of Van Gogh’s paintings.
David Lowery, director of last year’s A Ghost Story, wanted to trap his deceased title character in the boxy ratio. “It gave me a good opportunity to really hammer home the circumstances this ghost finds himself trapped in, and to dig into and break down the claustrophobia of his life within these four walls… And it was also a way to tap into some degree of nostalgia, because it feels old-fashioned when you see a movie in a square aspect ratio.”
4:3’s nostalgia factor has allowed it to be used very effectively for flashbacks, such as those in the recent Channel 4/Netflix series The End of the F***ing World. Wes Anderson delineated the three time periods of The Grand Budapest Hotel (2014) with different aspect ratios, using 1.37:1 for scenes set in 1932, the very same year in which that ratio was standardised by the Academy.
“Exit Eve”
Nostalgia, intimacy, claustrophobia, isolation – these are just some of the feelings which cinema’s original aspect ratio can evoke. For Charlie and I on Exit Eve, it was the sense of being trapped which made the ratio really fit our story.
I’m also a great believer in choosing a ratio that fits the shape of your primary location, and the converted schoolhouse which we were shooting in had very high ceilings. 4:3 allowed us to show the oppressive scale of these rooms, while giving the eponymous Eve little horizontal freedom to move around it. One additional practical consideration was that, when lensing a party scene, the narrower ratio made it easier to fill the frame with supporting artists!
It wasn’t hard to get used to framing in 4:3 again. A lot of Exit Eve was handheld, making for fluid compositions. There were a couple of tripod set-ups where I couldn’t help thinking that the extra width of 1.85:1 would be useful, but for the most part 4:3 worked well.
We were shooting on an Alexa Plus with a 16:9 sensor, meaning we were cropping the image at the sides, whereas ideally we would have hired a 4:3 model to use the full width of the sensor and a larger proportion of our lenses’ image circles. This would have allowed us to get slightly wider frames in some of the location’s smaller rooms.
Our sound department had to adapt a little. The boom op was used to being able to get in just above the actors’ heads, but with the generous headroom I was often giving, she had to re-learn her instincts.

I had forgotten how well dialogue scenes are suited to 4:3. With wider ratios, over-the-shoulder shots can sometimes be tricky; you can end up with a lot of space between the foreground shoulder and the other actor, and the eye-line ends up way off camera. 4:3 perfectly fits a face, along with that ideal L-shape of the foreground shoulder and side of head, while keeping the eye-line tight to camera.
Not every project is right for 4:3, far from it. But I believe that the ratio has served its sentence in the wilderness for its pan-and-scan crimes against cinema, and should now be returned to the fold as a valid and expressive option for filmmakers.
See also: